White Celuka PVC Foam Board - Rigid, Lightweight, and Durable Engineering Material
Product Characteristics
- Celuka Manufacturing Process: Produces a smooth, integral skin surface and a fine-celled, homogeneous core, resulting in superior screw holding capacity and edge finishing compared to sintered foam boards.
- Chemical Resistance and Waterproof: Inherently resistant to moisture, oils, and a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for humid environments and outdoor signage applications.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Provides exceptional rigidity and structural integrity while remaining lightweight, which is crucial for reducing shipping costs and easing handling.
Product Description
The White Celuka PVC Foam Board is a rigid, closed-cell sheet material manufactured through a continuous extruded (Celuka) process. This material is engineered to serve as a premium alternative to traditional materials like wood, aluminum, and acrylic, offering excellent machinability and environmental stability. Its primary design purpose is to provide a consistent, high-quality substrate for demanding fabrication and display applications.
This foam board is produced to high manufacturing standards, ensuring uniform density and consistent performance. It is a chemically inert, low-maintenance material that is resistant to impact, weathering, and degradation, offering a long service life and reliable performance in both commercial and industrial settings.
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Value / Description | Unit / Standard |
| Material Type | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | - |
| Core Type | Celuka (Integral Skin) | - |
| Standard Density | 0.55 | g/cm³ |
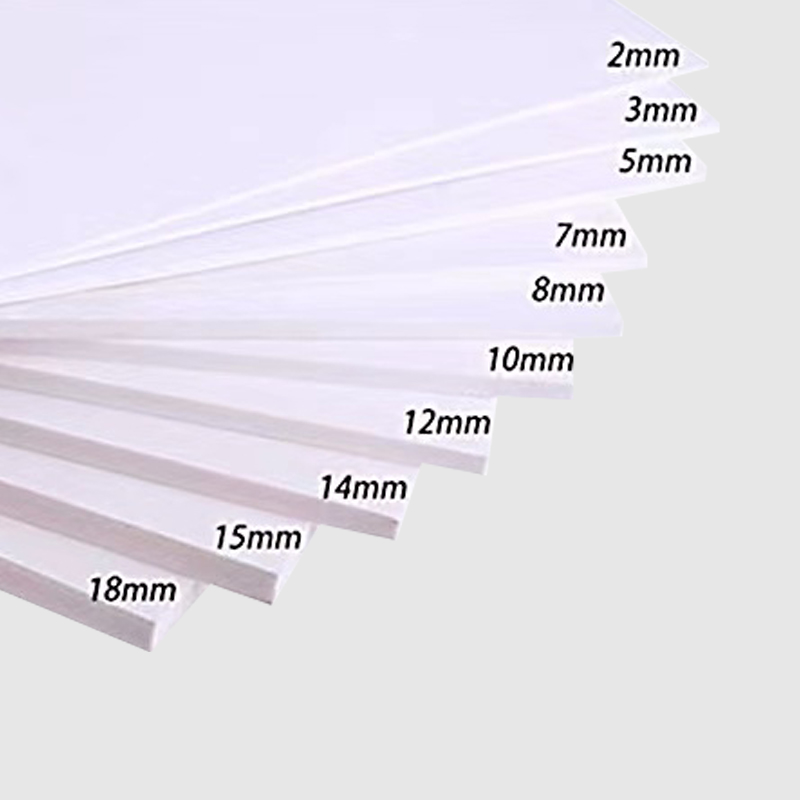
| Standard Thickness Tolerance | ±0.2 | mm |
| Water Absorption | < 1.0 | % (24h immersion) |
| Rockwell Hardness | 70 | R Scale |
| Tensile Strength | > 40 | MPa |
| Continuous Service Temperature | -20 to +60 | °C |
| Flame Retardancy | Self-extinguishing | UL94-V0 |
Application Fields
This product is suitable for the following industrial and commercial scenarios:
- Fabrication of point-of-purchase (POP) displays and exhibition stands
- Production of interior and exterior signage and nameplates
- CNC machining of prototypes, jigs, and fixtures
- Marine and vehicle interior paneling and cladding
- Architectural models and silkscreen printing substrates
Common Procurement Inquiries
1. How does Celuka PVC foam board compare to traditional foam core or Sintra for outdoor signage?
Celuka PVC foam board is significantly more durable than paper-faced foam core and offers superior performance to sintered PVC boards like Sintra for long-term outdoor use. Its non-porous, co-extruded skin provides a superior moisture barrier, preventing delamination and reducing water absorption. This results in better dimensional stability and resistance to warping under varying weather conditions. For a detailed comparison based on your specific environmental exposure, our technical team can provide a free material selection analysis.
2. What is the optimal method for bonding PVC foam sheets to other materials, and which adhesives are recommended?
For permanent, high-strength structural bonding of PVC foam board, we recommend using a two-component epoxy or a specialized PVC cement designed for rigid foams. These adhesives create a strong molecular bond with the substrate. For large-area laminations or applications requiring flexibility, a high-solids contact cement is often effective. The optimal method depends on the specific secondary material and load requirements. We provide a detailed technical datasheet with adhesive compatibility charts to all qualified clients.
3. Is this material suitable for high-precision CNC routing and milling, and what are the key parameters to prevent chipping?
Yes, Celuka PVC foam board is an excellent material for high-precision CNC machining. To achieve a clean, chip-free edge, use sharp, single-flute or triple-flute O-flute router bits specifically designed for plastics. Key parameters include maintaining a high feed rate and a moderate spindle speed to avoid melting the PVC. Using climb milling (down-cut) techniques can also help produce a superior finish. For complex projects, we recommend consulting with our engineering support team to optimize your machining parameters.


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى